




In the 1950s, the government of Mainland China "simplified" the written forms of many "traditional" characters in order to make learning to read and write the language easier for its then largely illiterate population.
Simplified characters may or may not be less pleasant to look at; however, the simplification project did succeed in making a more literate society. Whatever your opinion of outcome, this historical fact means we now have in print and on the Internet two sets of Chinese characters to deal with.
NOTELimiting yourself to just one set can be too, well, limiting. Just as you should become familiar with more than one system for romanizing Chinese pronunciation, learning both traditional and simplified characters will open up that many more resources for you. A good plan might be learning to read both sets, while focusing your writing efforts on just one at first.
NOTEKeep in mind too that not every character has been simplified, only some of the more complicated forms. Plus, this simplification of characters did follow some logical principles. Therefore, learning simplified characters alongside their traditional counterparts is not too difficult. For comparison, here is a list of examples. Traditional forms are on the left, followed by their simplified forms, pinyin pronunciation, and English equivalents.
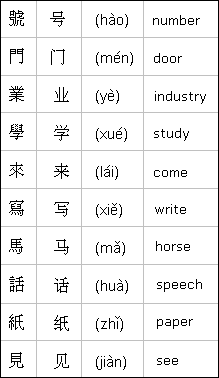
With the exception of the simplified character examples shown here, traditional characters are used throughout the rest of this site for two reasons.
First, Mainland China interacts more all the time with other Chinese-speaking regions where only traditional forms are used. As a result, Mainland Chinese professionals are increasingly willing and able to work with traditional characters, or fàn tĭ zì.
Second, they just look a heckuvalot nicer, don't they?
FOOD FOR THOUGHT